Understanding the Tier Country Classification System
When planning global digital advertising campaigns, marketers often categorize countries into tiers based on market maturity, digital infrastructure, and consumer purchasing power. This classification helps create tailored strategies that account for the unique characteristics of each market segment. In digital marketing and display advertising, tier countries refer to the classification of countries based on their economic development, purchasing power, and advertising value. This classification is mainly used in affiliate marketing, advertising networks, and global business strategies to determine cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-impression (CPM), and conversion rates.
The concept of tier countries in digital advertising refers to the classification of global markets based on several key factors:
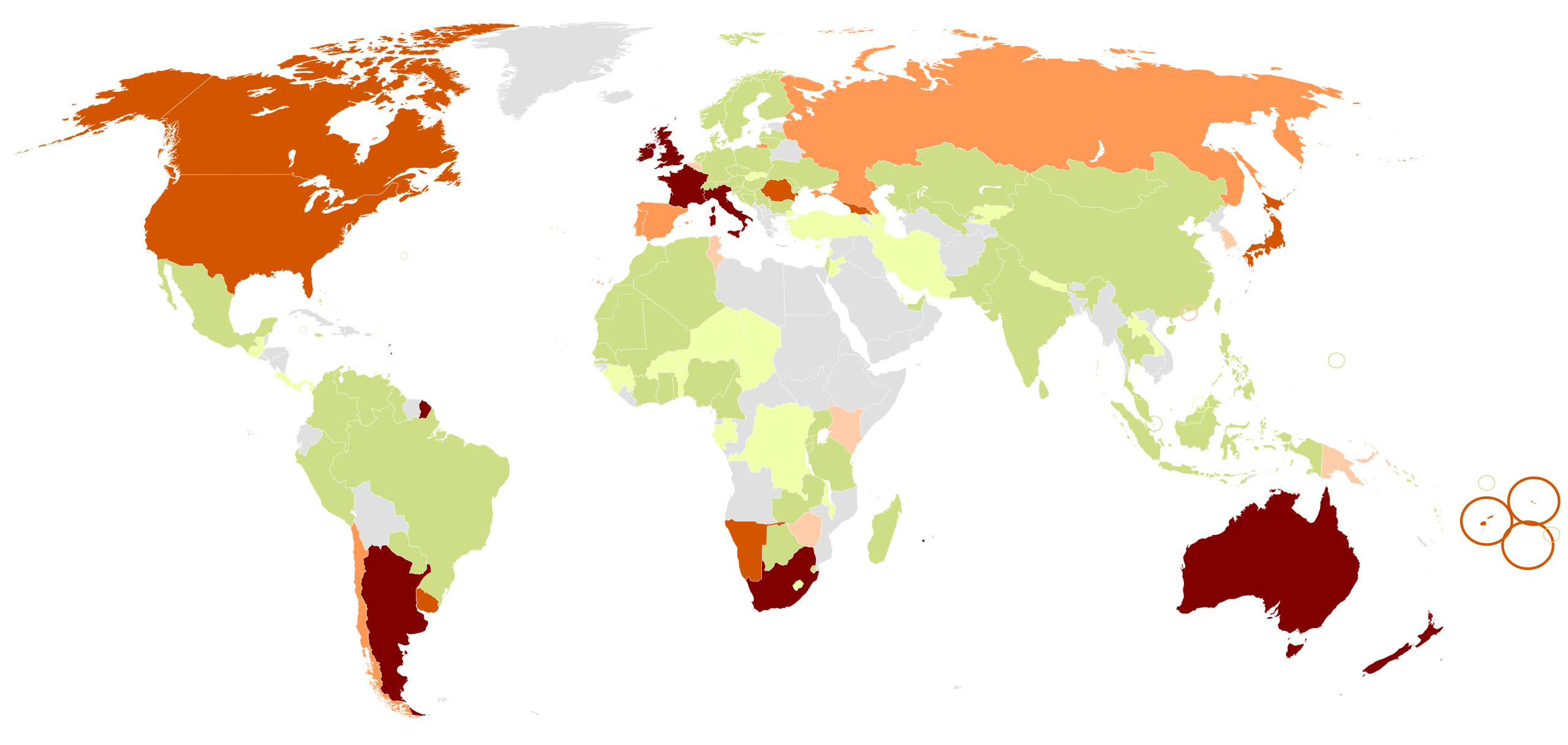
Tier 1 Countries: Highly developed economies with mature digital infrastructure, high internet penetration, and significant consumer spending power. Examples include the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Germany, Japan, and France. These markets typically feature high CPM (cost per mille) rates but offer sophisticated targeting capabilities and reliable measurement.
Tier 2 Countries: Emerging economies with rapidly developing digital ecosystems and growing middle classes. Nations like Brazil, Mexico, India, Turkey, Poland, Malaysia, and Thailand fall into this category. These markets offer a balance between reasonable advertising costs and substantial audience reach.
Tier 3 Countries: Developing economies with emerging digital infrastructure, increasing mobile adoption, and evolving consumer behaviors. Countries such as Vietnam, Nigeria, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Kenya represent this tier. While these markets present infrastructure challenges, they offer ground-floor opportunities for brands willing to invest early.
The Strategic Value of Tier-Based Display Advertising
Diversifying Market Reach
A tier-based approach to display advertising enables brands to diversify their market presence strategically. Rather than concentrating resources exclusively in highly competitive tier 1 markets, companies can distribute their advertising investments across different market categories to optimize both reach and efficiency.
For instance, a global e-commerce platform might allocate 50% of its budget to tier 1 countries where it faces established competition, 30% to high-growth tier 2 markets to capture emerging consumer segments, and 20% to select tier 3 countries where early brand positioning could yield long-term advantages.
Budget Optimization
The significant cost differential between tiers allows for creative budget allocation strategies. Display advertising CPMs in tier 2 countries typically range from 30-60% lower than in tier 1 markets, while tier 3 CPMs can be 60-80% lower. This cost efficiency creates opportunities for:
- Extended campaign durations in lower-tier markets
- Higher frequency caps to build brand recognition
- Broader audience targeting parameters
- More extensive A/B testing without prohibitive costs
Market Entry Pathways
For brands new to international expansion, tier-based advertising provides structured pathways for market entry. Companies can test concepts and messaging in select tier 2 or 3 markets before committing to more expensive tier 1 campaigns, gathering valuable insights while minimizing financial risk.
The Benefits of Display Advertising in Tier Countries
Cost-Effective Campaign Deployment
One of the most compelling advantages of display advertising in tier 2 and tier 3 countries is the significant cost efficiency. CPM (cost per thousand impressions) and CPC (cost per click) rates are typically much lower compared to saturated tier 1 markets. For example, advertising costs in tier 2 countries can be 40-60% lower than in tier 1 markets, while tier 3 countries may offer even greater savings of 60-80%.
This cost advantage allows brands to achieve greater reach and frequency with limited budgets, making these markets particularly attractive for companies looking to scale their digital presence efficiently.
Less Competitive Advertising Landscape
Tier 2 and tier 3 countries often feature less crowded advertising ecosystems. While major global brands have established presences in tier 1 markets, many have yet to fully commit to emerging economies. This creates opportunities for brands to capture market share, build brand recognition, and establish customer relationships before competition intensifies.
The reduced competition also translates to better placement opportunities and potentially higher engagement rates as consumers in these markets may experience less advertising fatigue.
Rapidly Growing Digital Audiences
Many tier 2 and tier 3 countries are experiencing explosive growth in internet penetration and digital media consumption. India, for instance, added over 100 million new internet users between 2019 and 2021, while countries across Africa are seeing similar digital expansion.
These growing audiences represent fresh opportunities for advertisers to connect with consumers who are experiencing many digital platforms and services for the first time – often leading to higher engagement rates and brand receptivity.
Testing Ground for New Strategies
Tier countries can serve as valuable testing environments for innovative campaign approaches before rolling them out in more expensive tier 1 markets. The lower stakes and costs allow marketers to experiment with creative formats, messaging strategies, and targeting parameters while gathering valuable insights.
Successful approaches can then be refined and scaled to other markets, creating a more efficient global campaign development process.
Challenges of Display Advertising in Tier Countries
Digital Infrastructure Limitations
While tier countries are making rapid progress in digital development, many still face infrastructure challenges. Internet connectivity in tier 3 countries may be inconsistent, with limited bandwidth and higher latency. Mobile networks may rely on older technologies, and power outages can disrupt online access.
These infrastructure limitations necessitate adaptations to campaign strategies, such as optimizing creative assets for lower bandwidths and designing mobile-first experiences that function effectively even with intermittent connectivity.
Payment Processing Complexities
The diversity of payment systems across tier countries creates significant complexity for advertisers, particularly those running e-commerce campaigns. Credit card penetration remains low in many tier 2 and tier 3 markets, with consumers instead relying on local payment methods, mobile money solutions, or cash-on-delivery options.
Successful campaigns must account for these payment preferences by integrating appropriate conversion paths and highlighting locally relevant transaction options.
Cultural and Linguistic Diversity
Tier countries represent incredibly diverse cultural contexts, each with unique values, preferences, and communication styles. What resonates in one market may fall flat or even offend in another. This diversity extends to language, with many tier countries featuring multiple official and regional languages.
Advertisers must invest in proper localization rather than simple translation, adapting messaging, imagery, and cultural references to align with local expectations.
Regulatory Variations and Compliance
Navigating the regulatory landscape across tier countries presents significant challenges. Digital advertising regulations vary widely, with some markets implementing strict controls on certain industries (like finance, healthcare, or gaming) while others maintain more open environments.
Data privacy frameworks also differ substantially, with some tier 2 countries adopting GDPR-like legislation while many tier 3 markets still developing their digital governance frameworks. Staying compliant across these varied regulatory environments requires careful market-by-market assessment.
Implementation Strategies for Display Advertising Success
Graduated Approach to Market Entry
Rather than simultaneously launching across multiple tiers, successful advertisers often implement a graduated approach:
- Foundation Phase: Establish campaigns in select tier 1 markets to refine messaging and operational frameworks
- Expansion Phase: Adapt successful strategies for tier 2 markets, incorporating learnings while adjusting for local conditions
- Frontier Phase: Selectively enter promising tier 3 markets with streamlined campaigns focused on brand building
This methodical progression allows organizations to develop institutional knowledge and operational capabilities that support successful multi-tier operations.
Technical Infrastructure Adaptations
To succeed across diverse technical environments, advertisers should prioritize:
- Implementing adaptive creative delivery systems that detect connection quality
- Creating multiple asset versions optimized for different bandwidth conditions
- Utilizing CDN (Content Delivery Network) solutions with global distribution
- Adopting cloud-based hosting for campaign assets to improve loading times
- Implementing lightweight tracking solutions for lower-tier markets
These technical adaptations ensure campaigns function effectively across varying infrastructure conditions.
Localized Buying Strategies
Media buying approaches should adapt to the unique characteristics of each tier:
- Tier 1: Leverage programmatic ecosystems, premium direct deals, and advanced audience targeting
- Tier 2: Balance programmatic with strategic publisher relationships and contextual targeting
- Tier 3: Emphasize direct publisher relationships, telecommunications partnerships, and simplified buying models
This tiered approach acknowledges the varying maturity of advertising ecosystems while maximizing effectiveness in each context.
Conclusion
Display advertising in tier countries represents a significant opportunity for brands seeking growth beyond saturated markets. While these regions present unique challenges related to infrastructure, payment systems, and regulatory complexities, the benefits of cost efficiency, reduced competition, and growing audiences make them increasingly attractive for global marketers.
Success in these diverse markets requires thoughtful adaptation rather than simple replication of tier 1 strategies. By embracing mobile-first design, forming local partnerships, and developing market-specific approaches, advertisers can effectively navigate the complexities of tier countries while capitalizing on their tremendous potential.
As digital transformation continues to accelerate across the globe, those who establish early positions in these emerging markets stand to gain substantial advantages in the evolving landscape of global digital advertising.







Leave a Reply